The CDC urges baby boomers to get tested for Hepatitis C, as new treatments are providing close to a 100% cure rate and you may not know you are infected. Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by a virus that can lead to chronic complications such as cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Cirrhosis is a result of liver disease that causes scarring on the liver and occurs when healthy tissue is replaced with scarred tissue.
According to a press release from the CDC issued in May of 2016, the number of deaths occurring from Hepatitis C reached record high numbers in 2014 at 19,659. A second study published by the CDC in Clinical Infectious Diseases reported that annual deaths from Hep C in 2013 surpassed the combined number of deaths from sixty other infectious diseases which include deaths by pneumococcal (flu) disease, tuberculosis and HIV. Add to this the fact that many cases of Hep C go unreported and the death toll is likely even higher, and still climbing.
There is no need to die from this curable disease. Get tested before symptoms appear, as many people go twenty years or more before showing symptoms that develop after liver damage has progressed.
Risk Categories for Hepatitis C
There are approximately 3.5 million people living in the United States with Hepatitis C, but because it can often pose no symptoms most people do not even know they have it. If symptoms do present, they are often stomach pains, nausea, vomiting and fever. It is highly recommended by the CDC to be tested if you are in any high-risk category, and especially if you are in the baby boomer generation born between 1945 and 1965.
Methods used for blood screening changed in 1992, so if you received a blood transfusion prior to 1992 you should also be tested. Intravenous drug users are at higher risk for contracting Hepatitis C, and contrary to some beliefs it is very rarely spread from tattoo parlors.
How is Hepatitis C Contracted?
Hepatitis C is contracted through bodily fluids and blood, infecting intravenous drug users that use or share needles, and it only takes one exposure to become infected. People in occupations such as nurses, doctors and police officers have to be especially careful as it is also contracted through an accidental needle poke. People can become infected through sexual contact, and infected mothers can pass the disease onto newborn babies.
Rarely someone may become infected by coming into contact with an infected person’s personal care items, although items such as razors and toothbrushes should not be shared or come into contact with others. Hepatitis C is not contracted through casual contact, food or water.
It is suspected that the number of medical procedures performed on those returning from World War II were done prior to blood screening methods used today, and many people had contracted and spread Hepatitis C without even knowing it. The baby boomer generation is experiencing the largest burden of reported cases and deaths caused by this now curable disease.
Hepatitis C Diagnosis and Treatment
Hepatitis C is diagnosed with a blood test, which is also used to determine the genotype. There are six genotypes and each responds differently to treatments. The majority of Americans with Hep C, about 75%, have Type 1 genotype. Blood tests are used to diagnose and monitor the disease with liver function tests that detect damage and inflammation of the liver.
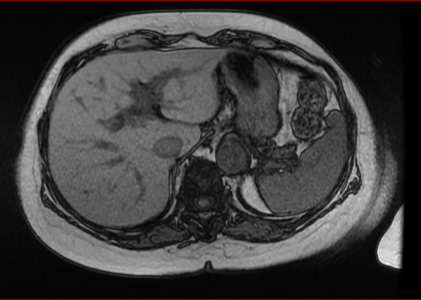
Your doctor may order additional imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan or MRI. Imaging is ordered especially if cirrhosis has developed to monitor the progression of the disease.
New Treatments for Hepatitis C
Treatments for Hepatitis C have come a long way, and as recently as January of 2016 the FDA approved a new drug called Zepatier which is a once daily pill combination currently offering close to a 100% cure rate. Harvoni is another once daily medication that often cures people within eight to twelve weeks. The most common side effects of these medications are headache and fatigue.
Prior treatments included injections and combinations of medications taken more than once per day with more side effects than the newer medications, while these new treatments offer once daily medications that cure people even quicker.
If you are in the baby boomer generation or any high-risk category, you should see your doctor to be tested for Hepatitis C. If you are living with this disease it is important to seek treatment before the condition worsens, and for monitoring any progression of liver damage.
It is especially important for anyone with Hepatitis C to avoid alcohol as that will accelerate liver damage, and speak to your doctor before taking any medication especially acetaminophen (Tylenol). It is always important to eat healthy and take care of yourself, and especially when living with a chronic liver disease.
Your friends at Greater Waterbury Imaging Center urge you to consult with your physician regarding testing for Hepatitis C if you are a baby boomer or in any high-risk category. Contact us with any questions and for all of your imaging needs.