American Diabetes Month: Supporting Awareness, Prevention, and Care

November marks American Diabetes Month, a dedicated time to raise awareness, encourage prevention, and provide education about diabetes. With 1 in 11 Americans—approximately 37 million people—living with this chronic condition, the importance of understanding diabetes and its impact cannot be overstated.
Whether you or a loved one is living with diabetes, support from family members, caregivers, and healthcare providers plays a crucial role in managing the condition and preventing complications. American Diabetes Month is an opportunity to learn more about how you can help yourself or someone you care about lead a healthier life.
Understanding Diabetes
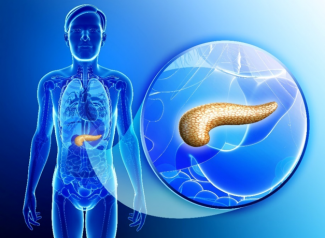 Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body regulates blood sugar (glucose), a vital energy source. Glucose levels in the bloodstream are managed by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When insulin production or function is impaired, glucose levels can rise to dangerous levels, leading to serious health complications.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body regulates blood sugar (glucose), a vital energy source. Glucose levels in the bloodstream are managed by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When insulin production or function is impaired, glucose levels can rise to dangerous levels, leading to serious health complications.
Resources from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) is a leading organization dedicated to advancing research and providing education on diabetes and other related health conditions. As part of National Diabetes Month, the NIDDK offers a comprehensive toolkit to support awareness and education.
This toolkit includes materials in both English and Spanish, making it accessible to a broader audience. It features printable fact sheets, social media content, and resources designed to educate individuals, families, and caregivers about diabetes management and prevention. These materials are invaluable for raising awareness and equipping communities with the knowledge to manage and prevent diabetes effectively.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
- Typically develops in children and adolescents when the pancreas fails to produce insulin.
- Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections or pump therapy to manage glucose levels.
- While less common, accounting for about 5% of all diagnosed diabetes cases, Type 1 requires vigilant management to prevent complications.
Type 2 Diabetes
- The more common form, Type 2 diabetes, usually develops later in life and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it.
- Modifiable risk factors such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management can significantly reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- For those diagnosed, lifestyle adjustments and medication can help manage the condition effectively. Learn more about Type 2 diabetes at the American Diabetes Association.
By understanding these types of diabetes and how they differ, individuals and caregivers can take proactive steps to manage or reduce their risk.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Understanding the risk factors for diabetes is essential for prevention and early detection. While some factors are beyond our control, many can be managed through lifestyle adjustments and regular health monitoring.
Type 1 Diabetes Risk Factors
- Family History: A close relative with Type 1 diabetes increases your risk.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults.
- Genetics: Specific genes are associated with a higher likelihood of developing Type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
- Family History and Genetics: Having a parent or sibling with Type 2 diabetes raises your risk.
- Age: While more common after age 45, Type 2 diabetes is increasingly seen in younger populations due to lifestyle factors.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a major risk factor.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to insulin resistance.
- Diet: Diets high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: These conditions often occur alongside diabetes and contribute to its development.
Gestational Diabetes Risk Factors
- Pregnancy: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and is more likely in women who are overweight, have a family history of diabetes or are over 25 years old.
- Previous Gestational Diabetes: Women who have experienced gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy are at higher risk of recurrence.
Prevention Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, and regularly checking your blood sugar levels can significantly reduce your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. For more information on diabetes prevention and management, visit the American Diabetes Association. Learn more about How to Prevent Diabetes and Vascular Complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Diabetes
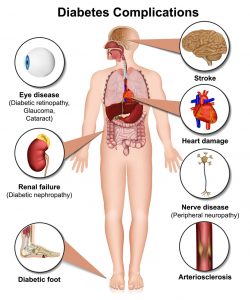
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for effective management and preventing complications. Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, extreme fatigue, and blurred vision. Some individuals may also experience slow-healing wounds or numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Learn more about the signs of diabetes and prevention strategies by visiting our blog: Learn the Symptoms and How to Prevent Diabetes.
The Role of Caregivers
Caregivers play a crucial role in supporting loved ones with diabetes, helping them manage daily challenges and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Monitoring blood glucose levels, preparing balanced meals, and encouraging regular physical activity are vital ways caregivers can assist.
Beyond physical health, caregivers also help promote mental well-being by providing emotional support and reducing the stress associated with managing a chronic condition. Their encouragement can empower individuals with diabetes to stay positive and motivated on their journey to better health.
Living with Diabetes: Tips for Prevention and Management

Managing diabetes requires a proactive approach, and these tips can help improve outcomes while enhancing overall well-being.
- Daily Monitoring: Regularly checking glucose levels and working closely with a healthcare provider to maintain control is essential. Consistent monitoring helps identify patterns and allows for timely adjustments in care.
- Healthy Eating:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains helps stabilize glucose levels. With the holidays approaching, individuals can enjoy meals while monitoring sugar intake. Explore the Diabetes Food Hub’s Thanksgiving Recipe Roundup for delicious, diabetes-friendly options. - Exercise:
Regular physical activity improves glucose regulation and supports overall health. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga are great ways to stay active. - Stress Management:
Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels. Incorporating mindfulness, meditation, or other stress-reducing techniques can improve mental health and glucose control.
National Resources and Support
Numerous organizations provide resources to support individuals with diabetes and their caregivers:
- The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) offers its National Diabetes Month Toolkit, including materials in English and Spanish to promote awareness and education.
- The American Diabetes Association provides Diabetes Month Resources, with educational tools, programs, and support for managing diabetes.
- Visit the main American Diabetes Association website for ongoing support, community involvement, and updated resources for individuals living with diabetes.
These resources empower individuals and families with knowledge and tools to manage diabetes effectively.
Enjoying a Healthy Thanksgiving with Diabetes-Friendly Meals
Thanksgiving is a time for celebration and delicious meals, but it can also present challenges for those managing diabetes. Fortunately, with a little planning and mindful choices, you can enjoy the holiday
feast while maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
The Diabetes Food Hub’s Thanksgiving Recipe Roundup offers a variety of diabetes-friendly recipes that combine traditional flavors with healthy ingredients. From savory roasted turkey to creative takes on classic sides like stuffing and mashed potatoes, these recipes focus on balance and taste. Desserts, such as low-sugar pies, allow you to indulge without compromising your health goals.
Key tips for a healthy Thanksgiving meal:
- Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables like green beans, Brussels sprouts, or a fresh salad.
- Choose lean proteins like turkey and limit heavy gravies or sauces.
- Practice portion control for carb-heavy dishes like stuffing, potatoes, and desserts.
- Stay hydrated and consider a light walk after the meal to support glucose regulation.

With these strategies and the Diabetes Food Hub’s resources, you can savor the holiday while keeping your health in check.
National Diabetes Month serves as a vital reminder of the importance of awareness, prevention, and management of diabetes. By adopting healthy habits, monitoring glucose levels, and utilizing available resources, individuals and their caregivers can take meaningful steps toward a healthier future.
Use this month to explore educational materials, connect with support networks, and consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing or preventing diabetes.
Greater Waterbury Imaging Center cares about your health and wellness and urges you to take the necessary steps to prevent diabetes or manage it well for those living with the disease. Contact us for all your MR imaging needs, for quality and compassionate care.