Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography MRCP
 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography MRCP is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exam which provides detailed images of the hepatobiliary and pancreatic systems. The organs which are typically studied in an MRCP exam are the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas and pancreatic duct.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography MRCP is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exam which provides detailed images of the hepatobiliary and pancreatic systems. The organs which are typically studied in an MRCP exam are the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas and pancreatic duct.
MRI is a noninvasive diagnostic imaging exam which medical professionals use to diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful magnet, radio frequency signals, and a sophisticated system to produce detailed images of internal anatomical structures such as organs, soft tissues, and bone. MRI does not use ionizing radiation or x-rays.
The detailed MR images make it possible to non-invasively study the internal structures of the body in order to determine the presence of certain diseases.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
Medical professionals use the MRCP study to:
- Examine diseases of the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas and pancreatic duct including looking for tumors, stones, inflammation or infection.
- Evaluate patients with pancreatitis to detect the underlying cause
- Help to diagnose unexplained abdominal pain
- Replacement to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) which international guidelines recommend ERCP only in cases where biliary intervention is required
MRCP Scan Technology at GWIC
- Previously motion-free, high-quality MRCP images were only possible if the patient remained perfectly still and held their breath during the acquisition of the images
- At GWIC, our Propeller technology combats patient motion by allowing free-breathing to ‘freeze’ the motion during breathing
- We are also able to minimize the amount of time that a patient has to hold their breath to 15 – 18 seconds if breath-hold is needed
- When imaging the liver, we can add a tracker to the dome of the liver which effectively ‘sees’ the rise and fall of the liver with breathing and only acquires the images when there is no motion
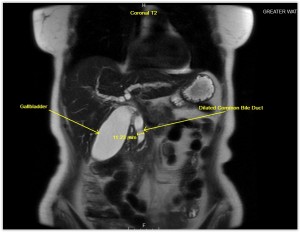
- This allows us to acquire these high-quality MRCP images seen in the following case study
Visit the clinical section of our website to view an MRCP Case Study.