What is the MRI Shoulder Scan?
MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is used to examine the shoulder joint in order to view the internal structures of the shoulder including the shoulder joint, the bones, tendons, muscles and blood vessels. All these structures can be seen in great detail with MRI and from any angle or plane or even in three dimensions (3D).
MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging exam, which helps healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat conditions of the shoulder joint. The MRI system is comprised of a powerful magnetic field, the production of radio frequency pulses, and sophisticated computer technology to show the detailed images of virtually all other internal body structures. Although similar in some ways to x-ray, MRI doesn’t use x-ray or have the dangers associated with x-ray or ionizing radiation.
Why is MRI Used for Evaluating Shoulder Joints?
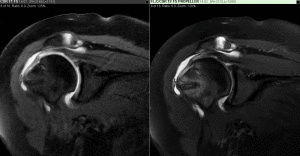
MRI for examining the shoulder joint provides very detailed views of common problems seen in the shoulder joint such as rotator cuff tears, tendon injuries, or damage to the soft fibrous tissue rim that helps stabilize the joint called the glenoid labrum.
MRI of the shoulder is normally ordered to diagnose or evaluate the following conditions:
- degenerative joint disease including arthritis
- fractures of the shoulder bones in some cases
- rotator cuff disorders such as tears
- joint problems due to trauma
- sports-related or work-related injuries
- infection in the joint
- tumors and metastases
- pain caused by swelling or bleeding in the joint area
- pain which is unexplained and does not respond to treatment
- decreased range of motion
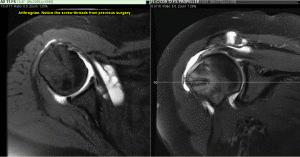
- evaluation after surgery
How is the Shoulder Scan Done?
Normally, an MRI of the shoulder is performed without the contrast material first, and several images of the area are obtained to evaluate the problem and gain information for a diagnosis. If a tear in the joint is suspected, then your physician may order an MR Arthrogram of the shoulder. The MR Arthrogram is the injection of contrast material into the shoulder joint space under fluoroscopic (x-ray) guidance. This assists the radiologist to better see the structures in the shoulder joint. Once the contrast is seen in the joint space under fluoroscopic guidance, the MR scan is performed on the patient. If there isn’t a tear, the contrast material should remain within the shoulder joint space and be absorbed into the tissue but if the contrast leaks out of the joint space, then the radiologist can determine the size and extent of any tears or other issues. To find out more about MRI exams and how to prepare for your exam, visit our patient section of the website or call us with any questions.
Greater Waterbury Imaging Center (GWIC) specializes in magnetic resonance imaging for patients in the greater Waterbury, CT area. Our goal is to provide you and your physician with a timely exam, a comfortable experience, and fast, accurate results. Physicians and patients throughout the greater Waterbury area rely on us to provide the highest quality MRI services. GWIC is located on the campus of Waterbury Hospital, adjacent to the Emergency Department. Park with ease for free in our own private gated parking area. If you are looking for an experienced and professional facility to have your MRI shoulder scan, contact us for more information or to set up an appointment for your patients call 203-573-7674.